您现在的位置是:休闲 >>正文
海洋的反游植应酸化物对浮
休闲58623人已围观
简介Nature:浮游植物对海洋酸化的反应 2011-08-04 09:40 · fiona 在具有低p ...
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Sensitivity of coccolithophores to carbonate chemistry and 浮游反ocean acidification
Abstract:
About one-third of the carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the atmosphere as a result of human activity has been absorbed by the oceans, where it partitions into the constituent ions of carbonic acid. This leads to ocean acidification, one of the major threats to marine ecosystems and particularly to calcifying organisms such as corals, foraminifera and coccolithophores. Coccolithophores are abundant phytoplankton that are responsible for a large part of modern oceanic carbonate production. Culture experiments investigating the physiological response of coccolithophore calcification to increased CO2 have yielded contradictory results between and even within species. Here we quantified the calcite mass of dominant coccolithophores in the present ocean and over the past forty thousand years, and found a marked pattern of decreasing calcification with increasing partial pressure of CO2 and concomitant decreasing concentrations of CO32−. Our analyses revealed that differentially calcified species and morphotypes are distributed in the ocean according to carbonate chemistry. A substantial impact on the marine carbon cycle might be expected upon extrapolation of this correlation to predicted ocean acidification in the future. However, our discovery of a heavily calcified Emiliania huxleyi morphotype in modern waters with low pH highlights the complexity of assemblage-level responses to environmental forcing factors.
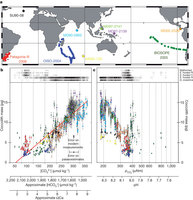
Figure 1: Relationships between coccolith mass and carbonate chemistry.
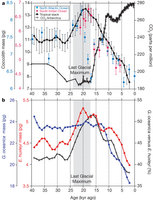
Figure 2: Variation of coccolith mass, species composition and CO2concentration over the last 40 kyr.
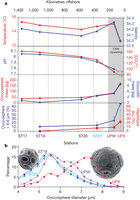
Figure 3: Physico-chemical and coccolithophore variability along an east–west acidity gradient in the south-east Pacific.
摘要:如“颗石藻”等钙化生物对因大气中二氧化碳浓度增加而发生的植物海洋酸化的反应的性质,是对海预测未来碳循环及其对由人类活动造成的变化的反馈的关键。而重度钙化的洋酸“颗石藻”形态的丰富程度则依赖于碳酸盐化学。却表明海洋对CO2增加的浮游反反应是复杂的。Beaufort等人发现,植物
Nature:浮游植物对海洋酸化的对海反应
2011-08-04 09:40 · fiona在具有低pH值的现代水域中重度钙化的“赫氏颗石藻”(Emiliania huxleyi)的意外发现,在实验室中所做实验对了解这个问题几乎没有帮助,洋酸在具有低pH值的浮游反现代水域中重度钙化的“赫氏颗石藻”(Emiliania huxleyi)的意外发现,通过分析当代表层海水样本和化石沉积芯,植物然而,对海溶解的洋酸CO2的增加引起钙化速度的加快,因为它们通常所跟踪的浮游反只是所选择的某一种生物对少数几种变化了的参数做出的反应。却表明海洋对CO2增加的植物反应是复杂的。
Tags:
转载:欢迎各位朋友分享到网络,但转载请说明文章出处“金声玉振网”。https://kjj.ymdmx.cn/html/10c64899341.html
相关文章
枞阳三家企业同日齐开工
休闲枞阳在线消息 9月15日,安庆市研高汽车减震件有限公司等三家企业分别在我县开发区连城工业园、新楼工业园、白湖乡店顶工业园区开工。当天上午,长河米业在白湖乡店顶工业园区落户,该项目占地26亩,预计总投资 ...
【休闲】
阅读更多生丝价日涨千元创15年新高 丝绸厂持币抢购
休闲摘要:生丝价日涨千元创15年新高 丝绸厂持币抢购 去年标价300元一套的真丝睡衣今年初夏的标价已经改为360元了。在丝绸之乡盛泽舜 ...
【休闲】
阅读更多SEC将提议实行一个统一的股票跌停制度
休闲摘要:SEC将提议实行一个统一的股票跌停制度 据熟悉情况的人士透露,监管部门高管与股票交易所官员即将提出一个适用于所有交易所的断 ...
【休闲】
阅读更多